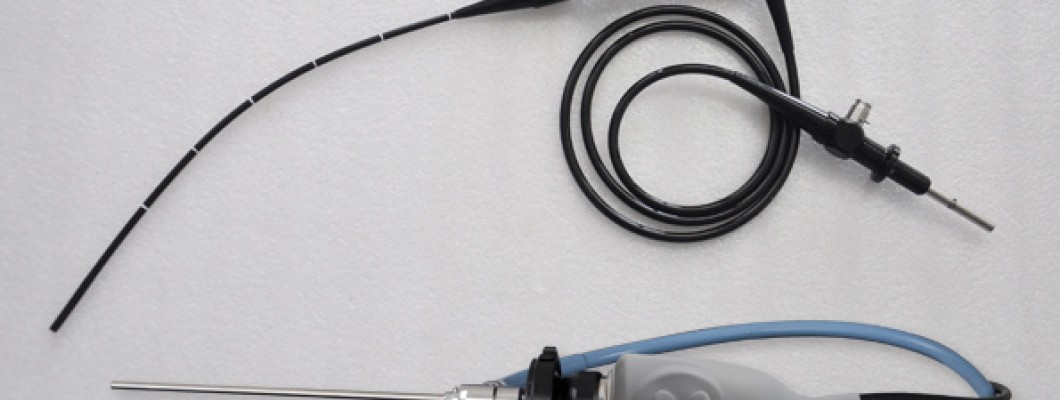
An endoscope, equipped with an image sensor, optical lens, light source illumination, mechanical device, etc., can enter the stomach through the mouth or enter the body through other natural channels, and directly observe changes in relevant parts. Helping doctors to comprehensively examine the condition inside the cavity and perform surgery under visual conditions greatly improves surgical safety.
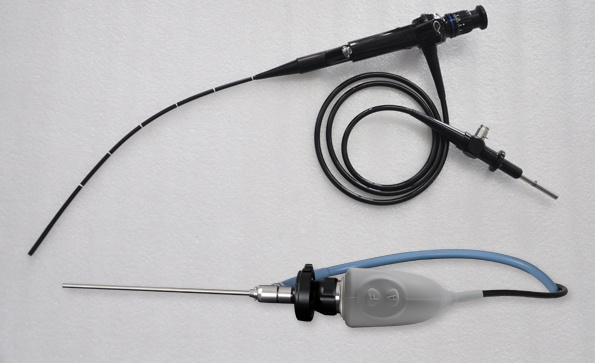
Endoscopes can be classified into three categories based on their development and imaging structures: rigid tube endoscopes, optical fiber (flexible tube) endoscopes, and electronic endoscopes. Many people cannot distinguish between rigid tube endoscopes and flexible tube endoscopes. What is the difference between rigid tube endoscopes and flexible tube endoscopes? Let's learn about it together below.
The difference between rigid tube endoscope and flexible tube endoscope:
1. Different appearance forms
Hard tube endoscope: The main body of the endoscope cannot be bent or twisted, and the depth and distance of the hard tube endoscope entering the body are much lower than those of the flexible tube endoscope;
Flexible tube endoscope: a type of endoscope with a flexible and bendable body.
2. Different internal structures
Hard tube endoscope: According to its structural form, it can be divided into four categories: straight rod non separable hard tube endoscope, straight rod separable hard tube endoscope, bent tube non separable hard tube endoscope, and bent tube separable hard tube endoscope. Various types of rigid tube endoscopic structures generally include an outer tube (or sheath), a mirror body, a light beam interface, a visual end connector, and an imaging interface part. Unlike soft endoscopes which have operating channels, some hard endoscopes do not have instruments or water vapor channels, such as laparoscopy, thoracoscopy, mediastinoscopy, arthroscopy, etc; Various surgical instruments need to be inserted into the body cavity through a separate incision, and the surgical operation is completed under the supervision and cooperation of a rigid endoscope.
Flexible tube endoscope: generally includes the following basic structures: front end, curved part, insertion tube, manipulation part, contact part, and imaging interface part. The front end is a rigid part, with multiple cavities and windows on the end face, including water and air supply outlet holes, biopsy forceps outlet holes, objective lens, and light guide window. Sending water and air is a common outlet. When injecting air, the gas enters the human body cavity through this hole to expand the cavity; When injecting water, the water comes out of this hole to rinse the objective lens and surgical field, keeping the field of view clear. The negative pressure suction and biopsy forceps have the same outlet hole. When there is too much liquid in the cavity that hinders observation, press the suction button, and the liquid can be sucked into the suction bottle through this hole; Biopsy forceps and other therapeutic instruments also enter the body cavity through this hole. The curved part is located between the front end and the insertion tube, and is composed of many circular parts forming a snake tube. Each pair of adjacent circular parts can move in various directions. Insertion tube, also known as mirror body or flexible tube, contains various types of pipes and steel wires inside. The control unit includes angle control knobs, suction valve buttons, water and air supply buttons, and biopsy tube openings. Surgeons can operate various buttons here to complete endoscopic examination and treatment.
3. Different application methods
Hard tube endoscope: mainly enters sterile tissues and organs of the human body or enters sterile chambers through surgical incisions, such as laparoscopy, thoracoscopy, arthroscopy, discoscopy, ventriculoscopy, etc.
Flexible tube endoscope: It mainly completes examination, diagnosis, and treatment through the natural cavity of the human body, such as gastroscopy, colonoscopy, laryngoscope, bronchoscope, etc. It mainly enters the human body through the digestive tract, respiratory tract, and urinary tract.
Hysteroscopy, cystoscopy, and colonoscopy all have soft and hard endoscopes.
The above is a brief introduction to the differences between rigid tube endoscopes and flexible tube endoscopes. Hard tube endoscopes and flexible tube endoscopes have differences in cleaning and disinfection processes, drying processes, storage methods, etc. Please feel free to consult for more information!
This article is compiled and published by Yikoda Endoscopic Camera for you. Please indicate when reprinting!










Leave a Comment